Inflammation - Acute can be a life saver, Chronic can lead to ill health
More than 50% of all deaths worldwide are attributed to chronic inflammatory diseases, including cancer, cardiovascular disease, dementia, stroke and diabetes. A report published by The Brainy Insights, the global anti-inflammatory drugs market is expected to grow from USD 95.23 billion in 2022 to USD 164.97 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 7.11% during the forecast period 2022-2030
Chronic Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) use can lead to severe kidney impairment due to its direct and indirect effects on the organ. The use of NSAIDs can increase blood pressure, cause fluid retention, and decrease kidney function in patients with kidney disease.
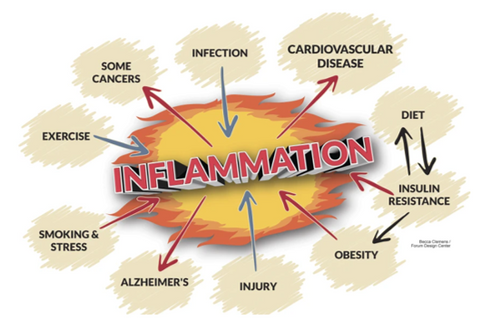
Inflammation is part of the body's defence mechanism. It is the process by which the immune system recognizes and removes harmful and foreign stimuli and begins the healing process. Inflammation can be either acute or chronic.
Acute inflammation: The response to sudden body damage, such as cutting your finger. To heal the cut, your body sends inflammatory cells to the injury. These cells start the healing process.
Chronic inflammation: Your body continues sending inflammatory cells even when there is no outside danger. For example, in rheumatoid arthritis inflammatory cells and substances attack joint tissues leading to an inflammation that comes and goes and can cause severe damage to joints with pain and deformities.
The most common reasons for chronic inflammation include:
- Autoimmune disorders, such as lupus, where your body attacks healthy tissue.
- Exposure to toxins, like pollution or industrial chemicals.
- Untreated acute inflammation, such as from an infection or injury.
- Allergies and food sensitivities
What are the symptoms of acute and chronic inflammation?
Acute inflammation may cause:
- Flushed skin at the site of the injury.
- Pain or tenderness.
- Swelling
- Heat
Chronic inflammation symptoms may be harder to spot than acute inflammation symptoms. Signs of chronic inflammation can include:
- Abdominal pain.
- Chest pain.
- Fatigue
- Fever
- Joint pain or stiffness. (example: rheumatoid arthritis)
- Mouth sores.
- Skin rash. (eg psoriasis)
|
Inflammation causing foods |
Inflammation reducing foods |
|
· Sugar · Cooking Oils – choose coconut oil or butter · Trans Fats – biscuits, margarines, shop bought cakes · Dairy Products · Red meat & processed meats · Alcohol · Refined Grains – while flour, white rice, white pasta, biscuits, pastries, etc · Artificial Food Additives – incl artificial sweeteners, MSG
|
· Tart Cherries · Lemon Juice · Turmeric · Cruciferous Vegetables – broccoli, cauliflower, spinach and cabbage. · Ginger · Oily fish · Shiitake Mushrooms · Green Tea · Pineapple · Papaya · Blueberry, cranberries, strawberries, raspberries, · Olive Oil |
If you would like to start your health journey today and get to the root cause of any symptoms you are experiencing, I would be delighted to work with you.

This blog is not intended to take the place of medical advice. Please seek assistance for any medical concerns.
